Sales Capabilities Required to Compete Today
Improving win rate

Building Selling Skills to Engage the Modern Buyer
In the virtual selling environment of today, sales professionals need a wider range of capabilities. By developing these diverse capabilities, sales professionals become more agile in their pursuits.
They are equipped to move with the increasing pace of change and adapt in the moment to the customer’s needs. Simply put, there is no single competency that drives sales excellence — rather, it is a collection of behaviours and skills across the selling process that needs to be honed and mastered.
Each of these capabilities falls into one of four categories: create, win, negotiate, and grow. These four segments represent the areas in which sales professionals need to be proficient throughout the sales cycle. These capabilities also prepare professionals to sell to both logic and emotion, an increasingly important part of compelling groups of stakeholders to purchase.
Here, we break down the skills that form each of these four sections.
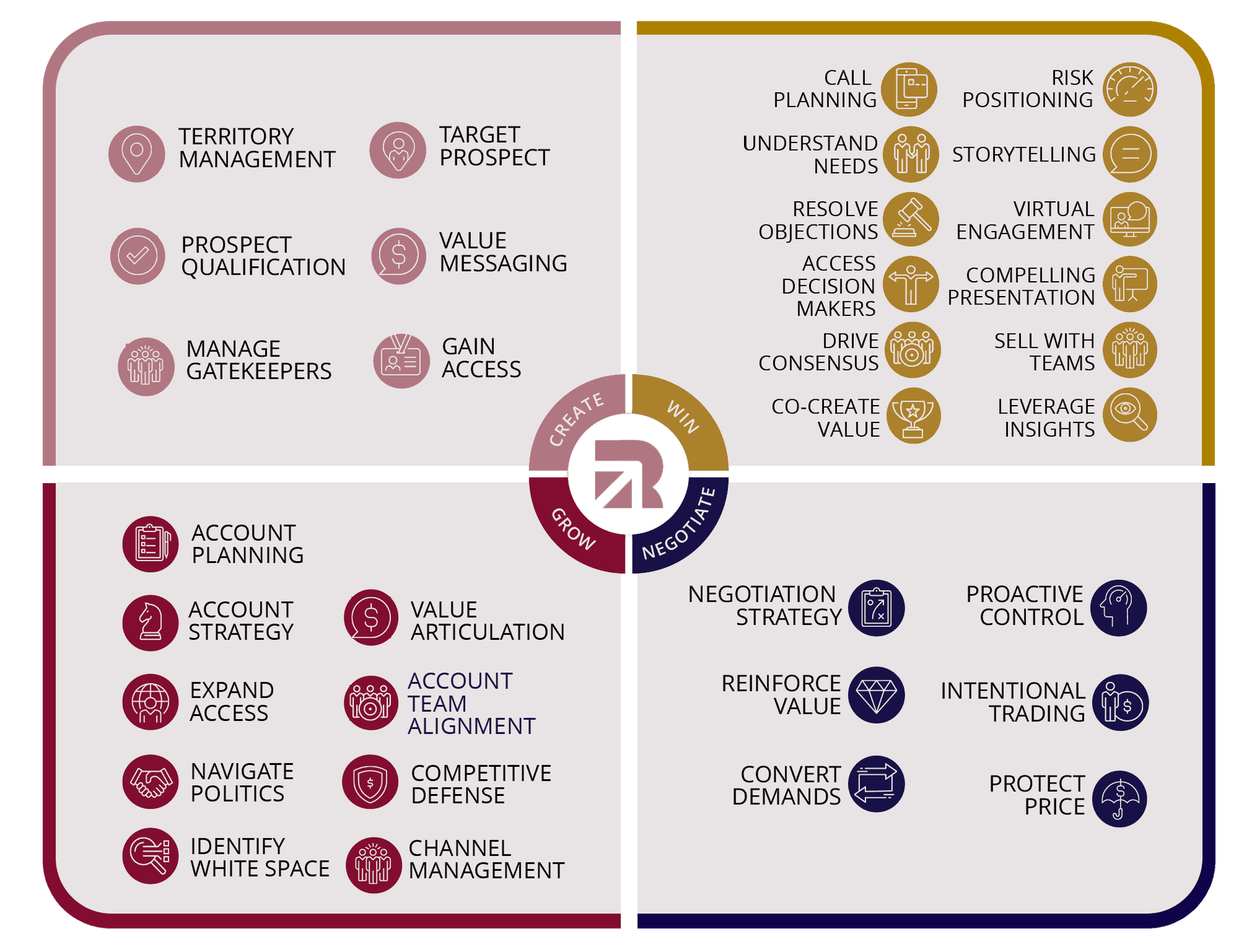
Create
Territory Management
Selling is more resource intensive than it has ever been. Therefore, sales professionals need a strategy that makes the best use of their time. Doing so means identifying the territories with the greatest potential, prioritising current customers and prospects, and creating a schedule that commits to a set of actions that includes prospecting, messaging, needs discovery, and follow-up.
Target Prospects
Next, sales professionals target their addressable market. Doing so means knowing common buyer profiles and identifying key prospects. This step requires understanding where the sales professional can offer meaningful value to customers who are prepared to buy.
Prospect Qualification
Sales professionals need to know if a prospect represents a viable opportunity. Answering this question requires an understanding of the prospect’s willingness to buy, the financial scope of the sale, and the potential long-term value of an ongoing relationship.
Value Messaging
Value messaging works when it addresses each stakeholder’s needs. To do so, sales professionals must first understand the full range of needs across all decision makers. Then, the sales professionals must articulate the solution’s value in ways that make the product or service feel at home in the context of the customer’s business.
Manage Gatekeepers
Managing gatekeepers requires transparency that leads to trust. Therefore, the sales professional must demonstrate authenticity in every conversation by sharing information. In many cases, the gatekeeper will respond to this approach by also sharing information that enables the sales professional to speak to the specific challenges and goals that will ultimately earn them the right to speak with higher-tier decision makers.
Gain Access
Gaining access means thinking beyond the solution. Sales professionals must spark the prospect’s interest by first speaking to the challenges in the customer’s world. To do so, sales professionals must seek out the industry information that is likely to be of interest to the contact. They must also seek out others in the prospect’s orbit and build rapport with that group to get a more current, detailed view of what is important to the prospect.
Win
Call Planning
The customer is under pressure and short on time. Therefore, call planning is critical for ensuring that the conversation offers value early. With preparation, sales professionals can leverage research to get to the core of the customer’s needs earlier in the call. The customer will not engage in a second conversation if the first one does not resonate.
Risk Positioning
Risk positioning means helping customers see that there is risk associated with any decision. Even the status quo presents risk because choosing not to move forward with a solution creates opportunity costs. Sales professionals must also show that risks can never be fully eliminated, but they can be calculated, right-sized, and outweighed by beneficial outcomes.
Understand Needs
As the sales professional begins to uncover customer needs and buying requirements, they can convert those requirements into insightful recommendations. The more detail they gain, the more effectively they can position the solution.
Storytelling
Emotions play into any decision. Therefore, sales professionals must be able to engage the client’s emotional drivers through compelling stories. They must be prepared to articulate the meaning of their solution with a narrative flow.
Resolve Objections
Objections are an inevitable part of the selling process. Rather than avoid them, sales professionals must have the capability to get to the root cause of the objection and position for a resolution. This skill is critical because it helps advance the sale without relinquishing terms or diminishing deal size.
Virtual Engagement
Effective virtual engagement means being able to communicate with customers from a distance. Sales professionals need the skills that get customers to openly discuss the full scope of their needs. This skill is critical to success in a digital setting in which distractions run high.
Access Decision Makers
Decision-making authority is spread across multiple stakeholders. Therefore, sales professionals must be able to track who has control over the different levels of the buying process as they seek access to the right people. This approach allows sales professionals to build consensus among stakeholders who are motivated by different factors.
Compelling Presentations
Buying decisions today come from numerous stakeholders working together. Therefore, sales professionals must be able to articulate their value and solution capabilities in a way that addresses multiple needs in accessible, clear language.
Drive Consensus
Building to a consensus is a process. Different stakeholders have various needs and perceptions of value. Sales professionals must be able to identify and navigate these group dynamics to engage and drive numerous stakeholders toward a decision.
Sell with Teams
When selling as a team, everyone must know their role and purpose. Everyone must be on the same page. Therefore, the leader of the team has the responsibility of developing unity among group members. Additionally, they often need to include an SME on the team and provide them with the guidance to perform in the unfamiliar setting of a sales conversation.
Co-Create Value
Fostering value co-creation requires getting the customer to articulate what aspects of the solution they believe are valuable. Reaching this point means refraining from jumping to solution positioning too soon. Sales professionals must take the time to connect business dependencies to the product or service.
Leverage Insights
With insights, the sales professional can reframe thinking. This is a powerful capability found in the most effective sales professionals. Many of the capabilities discussed above add up to this key skill, which is critical for overcoming the status quo, one of the biggest challenges for sales professionals.
Negotiate
Negotiation Strategy
It’s critical to confidently navigate the negotiation process to produce mutually beneficial outcomes. This capability is possible when the sales professional has strengthened their relationships, emphasised their value, and avoided any adversarial moves in favour of a collaborative approach.
Proactive Control
Controlling is the act of preserving the scope of the sale during negotiations. Exerting control allows the sales professional to find ways to address the customer’s pricing needs without reducing the size of the potential sale. This is a critical skill because it prevents the financial value of the deal from thinning in the final stages.
Reinforce Value
The seller must reinforce trust and credibility, even when negotiations are complete. When a seller follows up, they continue to demonstrate their competitive distinction and maintain momentum and customer respect. Reinforcing value is not just about the value of the solution — it is about the value of the people and interactions behind the solution.
Intentional Trading
Trading is one of the negotiator’s most powerful tools. It is powerful because it guards the negotiator against one of the most common traps in a negotiation: making a concession. The solution to this trap is a focus on trading. When a sales professional engages in trading, they are giving something and getting something in return. Put simply, trading is not unilateral — it is cooperative.
Convert Demands
Sales professionals must understand that demands are an expression of an underlying need. The power of a consultative approach is that it effectively reveals these needs through questioning. The key is remembering that needs are always easier to address than demands because a need can be satisfied in many different ways that do not necessarily limit the scope of the sale.
Protect Price
Protecting the price means understanding the root of the customer’s objection. In most cases, a demand for a lower price stems from another underlying issue. That issue might be payment terms, a misunderstanding about the value offered, or simply the customer’s need to feel heard.
Grow
Account Planning
To penetrate and expand business in customer accounts, sales professionals must become more strategic in how they enable accounts to create value. In addition, as sales cycles lengthen and involve more stakeholders in decisions, winning business requires more resources than ever before. By planning how to optimise account coverage with effective planning, salespeople can maximise revenue, growth, and win rates.
Account Strategy
Building an effective account strategy means developing a customised approach that addresses each decision maker’s unique set of needs and also differentiates solutions from competitive alternatives, including maintaining the status quo. An effective account strategy enables sales professionals to differentiate their value, not only by what they sell, but more importantly, by how they engage with customers.
Value Articulation
Sales professionals must be prepared to express the ROI of each solution meaningfully to different stakeholders. Value articulation begins with an accurate understanding of the customer’s needs. An effective questioning strategy is critical. Without this information, a sales professional will not be able to position the potential value of their product or service in a way that is useful to the customer.
Expand Access
With so many options available to buyers, it’s critical that sales professionals have the capability to build rapport and establish credibility with multiple stakeholders in an account. Building and developing customer relationships must be maintained because competitive pressures never end. By expanding access to decision makers, sales professionals can influence stakeholder alignment and build consensus during the buying process.
Account Team Alignment
Cohesion is what aligns account teams. Therefore, sales professionals need to understand how to deliver as a unified presence in front of a customer. Doing so means learning how to make seamless transitions from one sales professional to another, how to incorporate subject matter experts who are unaccustomed to selling, and how to keep messaging concise.
Navigate Politics
To properly navigate stakeholder politics in accounts, each sales professional must be able to tailor value conversations to different buying personas. The ROI factors that are important to the CFO will be different than those that are important to the COO. By accounting for these differences, sales professionals can develop broad buy-in for their solutions.
Competitive Defence
Demonstrating their ability to provide value consistently enables sales professionals to become go-to advisors in customer accounts. Reaching this trusted advisor status is important because it acts as a defence against less prepared competitors. Additionally, customers now have greater access to information than ever before. As a result, sales professionals must bring valuable insight that is above and beyond what the customer can access on their own.
Identify White Space
With an established customer relationship, it’s easier to grow business in an account than it is to source a new one. Sales professionals can work from an existing foundation to find the white space for developing new value and, therefore, discover new sales opportunities. With account planning, sales professionals can uptier and cross-sell their solution portfolio more effectively.
Channel Management
Each sales channel represents a unique business model with different costs, advantages, and limitations. Sophisticated selling organisations understand how to engage different channel partners to maximise coverage and provide value to different kinds of customers. Understanding channel partner differences also allows organisations to measure success and develop higher levels of sales productivity more effectively.
Success comes from this core group of capabilities that, as a whole, equips the sales professional to navigate an increasingly complex buying process. Each capability discussed above links to a specific part of the selling process, and as a result, sales professionals learn when and where they need to exercise each skill to build then maintain momentum to closing.The buyer journey has changed, and sales professionals need new capabilities to find, win, and grow accounts. In Richardson Sales Performance’s brief, Sales Capabilities Required to Compete Today, we list and define the seventeen specific skills for success in the market today. Complete the form to download the brief and discover why value propositions need to be customised to the stakeholders, how resolving objections protects the value of the sale, the importance of becoming a trusted adviser in the drive to grow an account, and increasing win rates by driving consensus.

Brief: Everything Begins with Soft Skills
Learn how to build the right selling skills for every role in your sales organisation.
DownloadGet industry insights and stay up to date, subscribe to our newsletter.
Joining our community gives you access to weekly thought leadership to help guide your planning for a training initiative, inform your sales strategy, and most importantly, improve your team's performance.






